Join Hands With Top Domestic And Foreign Expert Institutes
Jointly Build An Authoritative Platform For Neuroscience

 Knowing Nervonic Acid
Knowing Nervonic Acid

 Nervonic Acid Prospective Study
Nervonic Acid Prospective Study

 Retrospective Study
Retrospective Study
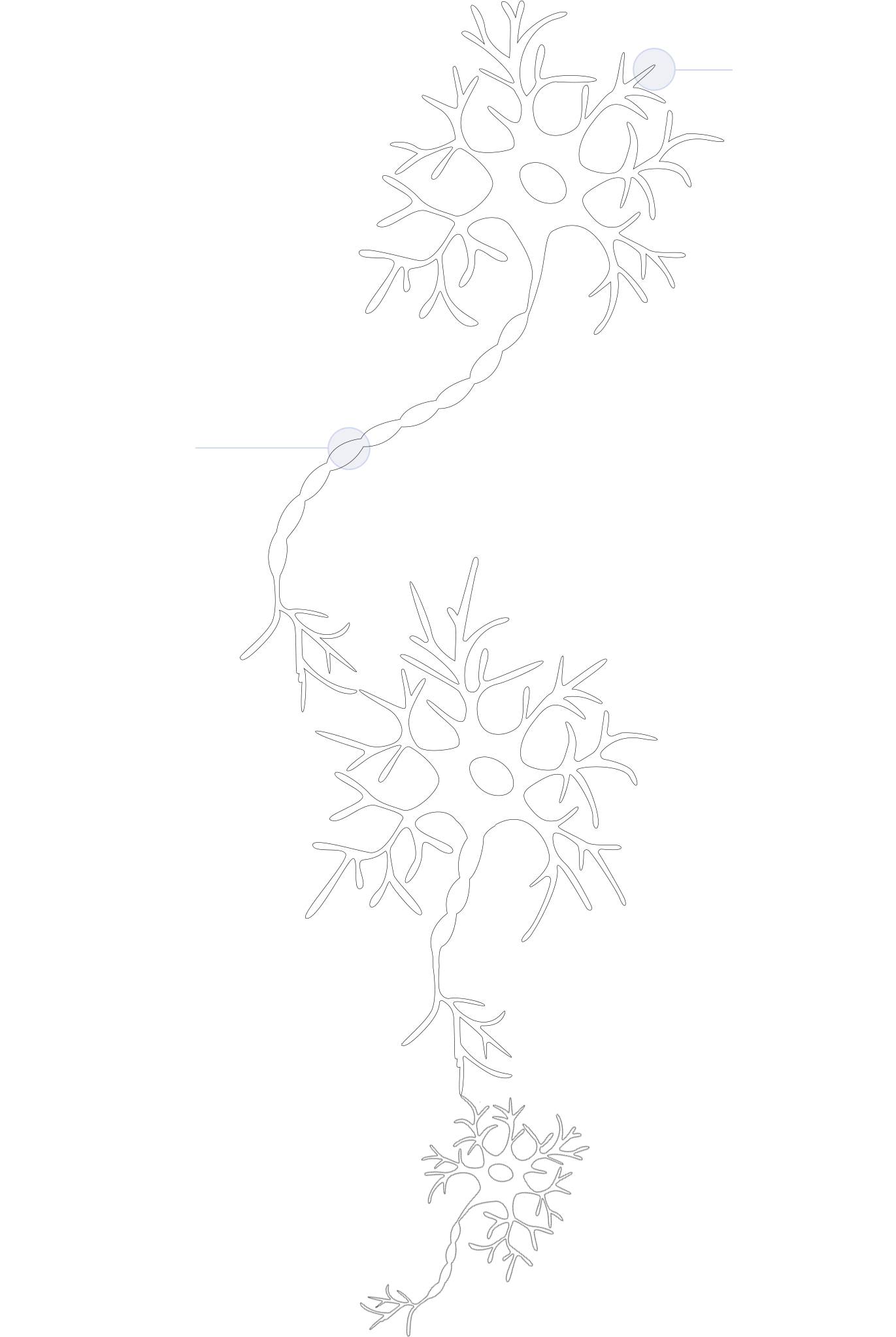
Dendritic
The nervous system in the human body is mainly responsible for transmitting and receiving information. Neurons, as the main cells of the nervous system, can sense changes in the environment, transmit information to other neurons, and instruct collective responses. Neurons account for about half of the nervous system, and most of them are composed of glial cells. Glial cells do not produce electrical impulses. They maintain homeostasis, form myelin sheath, and provide support and protection for neurons.
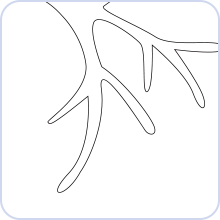
Myelin Sheath
The myelin sheath in the central system is formed by oligodendrocyte or other types of nerve supporting cells, 70% of which are composed of various lipids, which are wrapped around the axons of nerve cells to provide protection and support.
It is currently known that the function of myelin sheath can be roughly divided into three types:
1. Supporting the electrical insulation between axons and surrounding tissues, such as adjacent axons, to avoid interference in information transmission;
2. Providing " Saltatory Conduction " mechanism to speed up the transfer of action potentials.
3. Guiding the regeneration of axons when some axons are damaged.
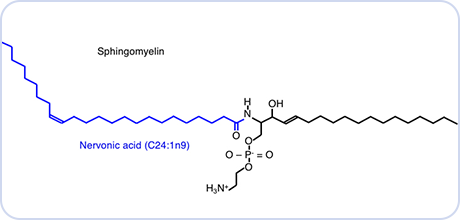
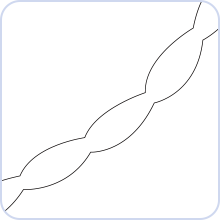
Nervonic Acid
Nervonic Acid (cis-15-tetracosenoic acid), also called selacholeic Acid. It is an important member of brain nerve cells, core components of nerve tissue and biofilm. Nervonic acid is implicated as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of nerve cell myelin. Nervonic Acid can promote the repair of nerve fibers in damaged brain tissues. It is also an essential "high-level nutrient" for the growth, redevelopment, and maintenance of nerve cells, especially brain cells, optic nerve cells, and peripheral nerves. Sphingomyelin accounts for about 40% of the fatty acids in the brain. According to current research, nervonic acid regulates the normal function of brain cell membranes in the brain and achieves the protective effect of maintaining the nervous system.
Reference:
Fan et al. 2018. Biosynthesis of nervonic acid and perspectives for its production by microalgae and other microorganisms. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8859-y
Content Abstract:
Nervonic acid (NA) is a major very long-chain monounsaturated fatty acid found in the white matter of mammalian brains, which plays a critical role in the treatment of psychotic disorders and neurological development. In the nature, NA has been synthesized by a handful plants, fungi, and microalgae. Although the metabolism of fatty acid has been studied for decades, the biosynthesis of NA has yet to be illustrated. Generally, the biosynthesis of NA is considered starting from oleic acid through fatty acid elongation, in which malonyl-CoA and long-chain acyl-CoA are firstly condensed by a rate-limiting enzyme 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase (KCS). Heterologous expression of kcs gene from high NA producing species in plants and yeast has led to synthesis of NA. Nevertheless, it has also been reported that desaturases in a few plants can catalyze very long-chain saturated fatty acid into NA. This review highlights recent advances in the biosynthesis, the sources, and the biotechnological aspects of NA.
Reference:
Lewkowicz, N, et al. (2019). Naturally Occurring Nervonic Acid Ester Improves Myelin Synthesis by Human Oligodendrocytes. Cells, 8(8), 786.doi.org/10.3390/cells8080786
Content Abstract:
The dysfunction of oligodendrocytes (OLs) is regarded as one of the major causes of inefficient remyelination in multiple sclerosis, resulting gradually in disease progression. Oligodendrocytes are derived from oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs), which populate the adult central nervous system, but their physiological capability to myelin synthesis is limited. The low intake of essential lipids for sphingomyelin synthesis in the human diet may account for increased demyelination and the reduced efficiency of the remyelination process. In our study on lipid profiling in an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis brain, we revealed that during acute inflammation, nervonic acid synthesis is silenced, which is the effect of shifting the lipid metabolism pathway of common substrates into proinflammatory arachidonic acid production. In the experiments on the human model of maturating oligodendrocyte precursor cells (hOPCs) in vitro, we demonstrated that fish oil mixture (FOM) affected the function of hOPCs, resulting in the improved synthesis of myelin basic protein, myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein, and proteolipid protein, as well as sphingomyelin. Additionally, FOM reduces proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, and enhances fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) synthesis by hOPCs was also demonstrated. Based on these observations, we propose that the intake of FOM rich in the nervonic acid ester may improve OL function, affecting OPC maturation and limiting inflammation.
Reference:
Wang, X. , & Wang, S. . (2010). Research status and application perspective of nervonic acid. China Oils and Fats. doi:CNKI:SUN:ZYZZ.0.2010-03-002.
Content Abstract:
Nervonic acid is the key component of nerve cells and tissues of brain, and it is the special material to promote the repair and regeneration of the damaged nerve cells and tissues. The chemical structure, bio-synthetic route, pharmacological effects and application status of nervonic acid were described, which could provide reference for the development of nervonic acid. The extraction of nervonic acid from vegetable oil was a sustainable development road.
Reference:
X Wang, Xie, S. , Wang, G. , Amp, N. A. , & University, F. . (2018). Application research status and prospect of acer truncatum Bunge.seed oil rich in nervonic acid in china. China Oils and Fats. doi:CNKI:SUN:ZYZZ.0.2018-12-022
Content Abstract:
Nervonic acid is the natural core component in nerve cells and nervous tissue in brain and has special physiological function and pharmacological action. Acer truncatum Bunge. seed oil rich in nervonic acid is the particular resource in China. The application research status and prospect of Acer truncatum Bunge. seed oil were summarized so as to promote the development of Acer truncatum Bunge. seed oil. The function of Acer truncatum Bunge. seed oil in human health, especially in brain health has drawn the attention of medical field in China, and the Acer truncatum Bunge. seed oil has the vital value for depth development.
Reference:
Li, et al. 2019. A mini review of nervonic acid: Source, production, and biological functions. J. Foodchem. 301, 125286. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125286
Content Abstract:
Nervonic acid (NA) has attracted considerable attention because of its close relationship with brain development. Sources of NA include oil crop seeds, oil-producing microalgae, and other microorganisms. Transgenic technology has also been applied to improve the sources and production of NA. NA can be separated and purified by urea adduction fractionation, molecular distillation, and crystallization. Studies on NA functionality involved treatments for demyelinating diseases and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, as well as prediction of mortality due to cardiovascular diseases and chronic kidney disease. This mini review focuses on the sources, production, and biological functions of NA and provides prospective trends in the investigation of NA.
Reference:
Qiuyue Ma, et al. 2020. The Acer truncatum genome provides insights into nervonic acid biosynthesis. Plant J. 104(3):662-678
Content Abstract:
Acer truncatum (purpleblow maple) is a woody tree species that produces seeds with high levels of valuable fatty acids (especially nervonic acid). However, the lack of a complete genome sequence has limited both basic and applied research on A. truncatum. We describe a high-quality draft genome assembly comprising 633.28 Mb (contig N50 = 773.17 kb; scaffold N50 = 46.36 Mb) with at least 28 438 predicted genes. The genome underwent an ancient triplication, similar to the core eudicots, but there have been no recent whole-genome duplication events. Acer yangbiense and A. truncatum are estimated to have diverged about 9.4 million years ago. A combined genomic, transcriptomic, metabonomic, and cell ultrastructural analysis provided new insights into the biosynthesis of very long-chain monounsaturated fatty acids. In addition, three KCS genes were found that may contribute to regulating nervonic acid biosynthesis. The KCS paralogous gene family expanded to 28 members, with 10 genes clustered together and distributed in the 0.27-Mb region of pseudochromosome 4. Our chromosome-scale genomic characterization may facilitate the discovery of agronomically important genes and stimulate functional genetic research on A. truncatum. Furthermore, the data presented also offer important foundations from which to study the molecular mechanisms influencing the production of nervonic acids.
Reference:
Wang, X. , & Wang, S. . (2010). Research status and application perspective of nervonic acid. China Oils and Fats. doi:CNKI:SUN:ZYZZ.0.2010-03-002.
Content Abstract:
Nervonic acid is the key component of nerve cells and tissues of brain, and it is the special material to promote the repair and regeneration of the damaged nerve cells and tissues. The chemical structure, bio-synthetic route, pharmacological effects and application status of nervonic acid were described, which could provide reference for the development of nervonic acid. The extraction of nervonic acid from vegetable oil was a sustainable development road.
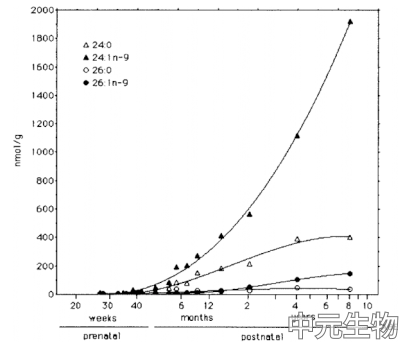
.
Reference:
X Wang, Xie, S. , Wang, G. , Amp, N. A. , & University, F. . (2018). Application research status and prospect of acer truncatum Bunge.seed oil rich in nervonic acid in china. China Oils and Fats. doi:CNKI:SUN:ZYZZ.0.2018-12-022
Content Abstract:
Nervonic acid is the natural core component in nerve cells and nervous tissue in brain and has special physiological function and pharmacological action. Acer truncatum Bunge. seed oil rich in nervonic acid is the particular resource in China. The application research status and prospect of Acer truncatum Bunge. seed oil were summarized so as to promote the development of Acer truncatum Bunge. seed oil. The function of Acer truncatum Bunge. seed oil in human health, especially in brain health has drawn the attention of medical field in China, and the Acer truncatum Bunge. seed oil has the vital value for depth development.

Hotline:400-086-9570

Beijing Headquarter:525 South building, Zhongguancun Medical Engineering Center for Health Industry Base
Shenzhen Office:World Trade Plaza, Fuhong Rd, Shenzhen
Hongkong Branch:Sun Hung Kai building, Wan Chai, Hong Kong
Copyright@2020 中元生物科技 版权所有京ICP备14045290号-6 ICP证书:京B2-20180057 技术支持:原创先锋

